How to Overcome Key Accounting Challenges in the Pharma Industry
Pharmaceutical industry accounting is complex due to high R&D costs, strict regulations, and long product life cycles. Each drug takes years to build, test, and sell. During this time, the money spent must be tracked well. From lab tests to market release, clear records are a must. If not, audits may fail, and money can be lost. This blog explains common challenges in the pharma industry that affect accounting tasks. We will also look at some quick and easy ways to fix them.
What Makes Pharmaceutical Industry Accounting Unique?
The pharmaceutical industry faces challenges that do not appear in other sectors. Its mix of science, long product cycles, and tight laws makes pharmaceutical industry accounting very different.
Long Research and Trial Time
Drugs take years to create. Trials and approvals stretch timelines. Pharma accounting must track every cost from lab work to approval. This helps plan budgets and control waste.
High Risk and Uncertain Results
Most drugs fail before they reach the market. Still, firms invest millions. Accounting must reflect this risk while keeping clean records for audits and board reviews.
Complex Global Rules
Drug companies sell across many countries. Each place has unique tax rules and report formats. These global gaps add more pressure to the daily accounting challenges faced in the pharma industry.
Large Product Lines
Pharma firms manage hundreds of drug SKUs. Each drug has a different cost, supply flow, and sale price. Firms must track all these layers to report the right profit.
Strict Testing and Approval
Before sales begin, drugs go through tests and checks. Each step costs money. If accounting misses any cost, audits may fail. Full records keep the firm safe and audit-ready.
The Role of Technology in Modern Pharmaceutical Accounting
Technology helps solve many challenges tied to the pharmaceutical industry accounting. With the right tools, companies can keep records accurate, meet rules, and manage fast-moving operations with ease.
Cloud-Based ERP Systems
Cloud systems let teams access real-time financials, cost data, and stock updates. They reduce time and improve transparency across departments.
Real-Time Dashboards
Dashboards give live updates on key numbers. Finance and R&D teams can quickly see cost spikes, project delays, or budget gaps.
AI-Powered Tools
AI helps sort massive data faster than humans. It finds errors, predicts risks, and improves the speed of report creation.
Secure Data Backups
Strong data backups prevent loss in case of cyberattacks or errors. Cloud security features also ensure that only the right users access records.
Compliance Features Built-In
Modern software includes compliance tracking tools. These help monitor rule changes and update workflows without needing manual checks.
Key Challenges and Solutions in Pharmaceutical Industry Accounting
There are multiple challenges in the pharma industry that impact accounting. These gaps affect decision-making, compliance, and daily operations.
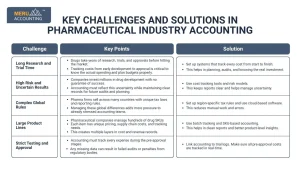
Challenge | Key Points | Solution |
Long Research and Trial Time |
|
|
High Risk and Uncertain Results |
|
|
Complex Global Rules |
|
|
Large Product Lines |
|
|
Strict Testing and Approval |
|
|
Improving pharmaceutical industry accounting takes focus and the right systems. These steps help firms fix gaps and build a solid setup.
Impact of Regulatory Compliance on Financial Accuracy
In the pharmaceutical space, staying compliant is not optional. Rules change often, and companies must keep accurate financials to avoid penalties.
FDA and Global Watchdogs
Regulators like the FDA and WHO not only inspect drugs but also how firms track R&D costs and revenues. Reports must meet strict audit standards.
Rules for Drug Prices
Some countries limit how much a company can charge for medicine. This forces accounting teams to adjust entries and maintain transparent pricing logs.
Detailed Audit Needs
Regulators may ask for every record from lab research to market release. Pharma accounting must store this data in a clear and searchable format.
Risk of Big Fines
Inaccurate records can result in massive fines or legal actions. Staying compliant protects reputation and ensures ongoing operations.
Law Shifts Over Time
New laws may change how costs are recorded or taxes filed. Accounting systems should allow quick updates to meet new legal standards.
Cost Control in R&D and Manufacturing
Keeping R&D costs under control is key in pharma. Without accurate tracking, firms may waste millions and face budget shortfalls.
Track All R&D Costs
Each test, trial, and lab session should be documented with date, purpose, and cost. This ensures every penny is counted during the audit.
Split Capital and Expense
Some R&D costs can be capitalized while others are expenses. Distinguishing them helps in proper reporting and managing future tax liability.
Avoid Cost Overruns
Set spending limits for each project. Use software alerts to notify managers when budgets approach thresholds. This avoids last-minute panic.
Streamline Procurement
Use digital systems to approve and track lab supplies and tools. It helps reduce duplicate orders and improves cash flow management.
Use Standard Rates
Set average cost values for repeat tasks like lab tests or site visits. This brings uniformity to reports and simplifies audits.
Case Example: How Strategic Accounting Solved a Pharma Firm’s Bottlenecks
A mid-size pharma company struggled with late books, audit issues, and high R&D costs. Here’s how they fixed the problem with strategic steps.
Step 1: Switched to Cloud ERP
Moving to the cloud allowed their team to access reports and dashboards anytime. This reduced reporting delays by more than half.
Step 2: Hired Pharma-Focused Accountants
Experts helped set up accurate cost codes, tax strategies, and better inventory tracking. This improved budgeting and cost clarity.
Step 3: Made Weekly Dashboards
With real-time data, teams could track stock levels, lab costs, and revenue trends. It supported faster decisions and planning.
Step 4: Linked Labs and Finance
Integrating lab tools with finance systems meant fewer errors. Costs were auto-logged into the right account with zero manual entry.
Step 5: Cut Delays by 40%
In six months, financial delays dropped, audit scores rose, and R&D waste was cut by a large margin.
Meru Accounting offers trusted solutions to solve all challenges in the pharma industry accounting. We help pharma firms stay focused on science while we handle the books. Our team understands pharma-specific needs. From R&D tracking to global tax filing, we offer support that fits your world. From cost breakdowns to real-time profit reports, we handle every step of pharmaceutical industry accounting with care.
FAQs
- Why is accounting in the pharmaceutical industry complex?
Because it involves long R&D cycles, strict laws, and global cost tracking. - What are common pharma accounting errors?
Manual entries, missed trial costs, and slow financial reporting. - How can firms reduce R&D accounting errors?
By using cloud tools, automating records, and setting clear budgets - What role does compliance play in pharma accounting?
It ensures accuracy, avoids legal issues, and supports audit readiness. - Can accounting tools help with cost control?
Yes, tools track spending, set alerts, and cut waste in real time. - How often should pharma firms close their books?
Monthly book closure helps spot errors early and improve control.


