What is an IRS Form 1040?
It is very important for a person residing in the USA to file their annual income tax returns using the 1040 form as per IRS guidelines. The IRS Form 1040 is an important document for individual taxpayers when filing income tax returns. This form is an official document to be submitted by U.S. taxpayers. There are different sections in this form where you can mention the standard deduction and income. It helps to understand the refund being received and the amount of tax owed. An individual may also have to attach additional forms called schedules, as the type of income gained. There are various types of schedules in Form 1040, as on the criteria satisfied.
What is IRS Form 1040?
IRS Form 1040 is the standard federal income tax form that individuals use to file their annual tax return with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Every year, millions of U.S. taxpayers fill out this form to report their earnings and determine whether they owe more taxes or are eligible for a refund.
You must use Form 1040 to report:
- All income earned during the tax year (such as wages, salaries, dividends, interest, freelance income, rental income, and capital gains).
- Adjustments to income like student loan interest or contributions to retirement accounts.
- Deductions and credits that reduce taxable income or tax liability.
- Payments already made, such as tax withholding or estimated tax payments.
Why is Form 1040 Important?
1. Mandatory Filing for Most U.S. Taxpayers
If your income exceeds a certain level or meets other conditions like self-employment income, you’re legally required to file the IRS Form 1040. It is a key part of staying compliant with U.S. tax laws.
2. Comprehensive Income Reporting
Form 1040 allows you to report all sources of income in one place:
- W-2 income from employers
- 1099 income from freelance or gig work
- Interest and dividends from savings and investments
- Business or self-employment income
- Rental or real estate income
- Social Security benefits and retirement distributions
The 1040 form acts as a complete summary of your earnings and financial activity for the year.
3. Helps Claim Refunds
If your employer withheld more tax than necessary or you made excess estimated payments, you can claim a refund using Form 1040. You may also receive refundable tax credits like:
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- American Opportunity Credit (for education expenses)
These credits can result in a refund even if you owe no tax.
4. Prevents IRS Penalties
Filing the IRS Form 1040 on time helps you avoid:
- Late filing penalties
- Interest on unpaid taxes
- Possible enforcement actions (e.g., IRS collections)
It’s also your defense in case of an IRS audit—you can show proof of accurate reporting and timely filing.
5. Foundation for Other Tax Forms
Many other IRS schedules and forms are directly connected to the 1040 form. Depending on your tax situation, you may need to attach additional forms like:
- Schedule 1: Additional Income and Adjustments
- Schedule 2: Additional Taxes
- Schedule 3: Additional Credits and Payments
- Schedule A: Itemized Deductions
- Schedule C: Profit or Loss from Business (self-employment)
- Schedule D: Capital Gains and Losses
All of these forms feed into the main Form 1040.
What is the main purpose of IRS Form 1040?
A proper calculation of the tax on the taxable income is mentioned in IRS Form 1040 by the taxpayers. A calculation of the Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) must be done initially. After this, the necessary allowable adjustments are made, which are also called above-the-line deductions. More deductions can be done with either itemized deductions as per Schedule A or the standard deduction. Expenses included in the itemized deductions are sales tax, state & local income taxes, mortgage interest, contributions made for charity, excessive medical expenses, etc. From 2018, the exemption deductions have been replaced with different dependent tax credits and child tax credits.
There are two main pages in the IRS Form 1040, excluding any attached schedules. The first page, in particular, collects the information about the dependents and the taxpayers. On this page, the filing status is specified by the taxpayers. The second page calculates the standard deductions allowable, income reporting, taxable income applicable after adjusted income, etc. On the right side of the first page, the fund check off of the presidential election campaign is there, and this is received by a Presidential election campaign fund.
Who needs to file Form 1040?
The losses or income made in only specific types must be filed on a 1040 form. Some of these include:
- Income received as shareholders in an S corporation, a partner in a partnership firm, a trust, or an estate beneficiary.
- Getting an income of $400 or more through self-employment.
- Dividends on the income tax policy than the premiums paid.
- Interest paid or received on the securities on certain terms.
- Had a qualified Health Savings Account from an IRA.
Apart from these, there are other aspects where you need to file Form 1040.
How to fill out Form 1040?
The 1040 form, provided by the IRS, can be downloaded and filled out manually or through software. However, now popular tax software is used for filling this form. This software can help you fill out the form with proper guidance. You can choose either of the ways, and the structure of the form will be common here. While filling out the form, it is important to gather proper tax documents like 1099s, W-2s, and other records of deductions and income.
You will have three options to fill out this form:
- Doing it yourself with the tax software.
- Doing it yourself with an IRS-free file.
- Outsource this work to a paid tax preparer
If you have proper experience and knowledge about it, then you can choose either of the first two options. However, if you have less knowledge or want to relieve yourself from this extra task, then outsourcing it to an expert tax preparer can be better. Here, tax professionals will have the expertise to fill out the Form properly. They can calculate appropriate taxes on the taxable income in a standard way. You can get an expert solution for tax preparation.
Key Sections of Form 1040
Let’s break down the important sections of the 1040 form:
1. Personal Information
- Name, SSN, address, and filing status.
2. Income
- Report all sources of income.
3. Adjustments to Income
- IRA deductions, student loan interest, etc.
4. Tax and Credits
- Child Tax Credit, Education Credits, etc.
5. Other Taxes
- Self-employment tax, household employment tax.
6. Payments
- Withholding from your paycheck, estimated tax payments.
7. Refund or Amount Owed
- Shows if you get a refund or have to pay more tax.
Important Schedules with IRS Form 1040
When you file IRS Form 1040, you may need to add more forms called schedules. These forms give extra info for income, tax, or deductions not shown on the main form.
Schedule 1 – Additional Income and Adjustments to Income
This schedule is for income not listed on Form 1040.
It includes income like:
- Unemployment pay
- Alimony received (for divorces before 2019)
- Gambling money
- Rental income
- Business income from a partnership or S corporation
It also includes:
- Student loan interest deduction
- Educator costs
- IRA or HSA contributions
- Alimony paid (for divorces before 2019)
Schedule 2 – Additional Taxes
This schedule is used to show taxes not on the main 1040.
It includes:
- Self-employment tax
- Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)
- Household worker taxes
- Extra tax on IRAs or retirement plans
- Repaying the Premium Tax Credit
Schedule 3 – Additional Credits and Payments
This form helps you claim more credits and payments.
It includes:
- Foreign tax credit
- Education credits
- Child and dependent care credit
- Saver’s credit
- Energy credit for your home
- Extra Social Security tax paid
Schedule A – Itemized Deductions
Use this if you itemize your deductions instead of using the standard one.
You can deduct:
- Medical and dental bills
- State and local taxes (up to $10,000)
- Mortgage interest
- Gifts to charity
- Losses from a disaster
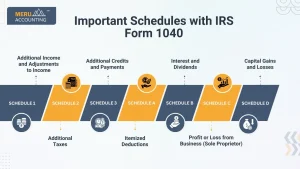
Schedule B – Interest and Dividends
You must use this if you earn more than $1,500 from interest or dividends.
It shows:
- The banks or companies that paid you
- The total you earned
- If you had a foreign bank account or trust
Schedule C – Profit or Loss from Business (Sole Proprietor)
This is for people who work for themselves.
It reports:
- Business income
- Costs like ads, rent, travel, or supplies
- Profit or loss from the business
Schedule D – Capital Gains and Losses
Use this to report gains or losses when you sell assets.
It includes:
- Stocks
- Bonds
- Mutual funds
- Crypto
- Property you don’t live in
This form splits short-term and long-term gains, which are taxed in different ways.
The 1040 form is essential for tax filing in the U.S. It’s used by nearly every taxpayer. Whether you’re employed, self-employed, or retired, you need to understand this form.
If you need help with your IRS Form 1040, Meru Accounting is here for you. Our experts ensure your return is accurate, timely, and stress-free.
Meru Accounting provides expert services for filling out the IRS Form 1040 when filing your income tax return. Meru Accounting Agency provides different accounting services across the world.
FAQs
Q1. What is a 1040 form?
It’s the main form used to file individual income tax returns in the U.S.
Q2. Who must file IRS Form 1040?
Any U.S. individual who meets income limits or has tax reporting needs.
Q3. Can I file Form 1040 online?
Yes, through IRS Free File or tax software.
Q4. Is IRS Form 1040 free to file?
Yes, the form is free; you may pay for help or software.
Q5. What happens if I file late?
You may face penalties and interest on unpaid tax.
Q6. Do I have to attach all schedules?
Only attach schedules that apply to your situation.
Q7. What if I made a mistake on Form 1040?
File an amended return using Form 1040-X.


